Hardware Setup Support: MacOS Serial Port connections
Limitations
Newer MacOS and OS X hardware come without a built in
RS232 serial port but provide USB ports.
Connect a serial DCC Adapter using a USB-to-Serial Adapter.
Connecting
Wiring
Macintosh serial ports used a "mini DIN-8" connector, which does not contain all of the signals of a typical RS232 connector. This page discusses how to wire an adapter so that a Macintosh can work with JMRI and a LocoBuffer or LocoBuffer II. The same adapter may also work with other protocols, particularly those that use "hardware flow control".
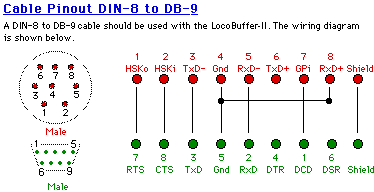
Note that the Macintosh has only one status output and input.
If the serial device uses "hardware flow control", it will assert the CTS lead to indicate when it's OK to send data. That has to be connected to the Macintosh input lead, or the program won't be able to send.
The status output will be set active by JMRI at startup. It should be connected to whatever status leads (e.g. RTS) the serial device looks at.
Documentation
Third Party info
A good survey of (Macintosh) serial connections, including debugging techniques, is available at:
- http://www.applefool.com/se30/#serialdata
- http://maxembedded.com/2013/09/serial-communication-rs232-basics/#SerialTerm
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Serial_port provides general information
- http://permalink.gmane.org/gmane.os.netbsd.ports.macppc/7467 provides a simple pin out
Credits
The information on this page was provided by Dick Bronson and Walter Thompson.
